Join Us On:Facebook: Google +: https://plus.google.com/u/0/b/5/11648. Hypochromia means that the red blood cells have less color than normal when examined under a microscope. This usually occurs when there is not enough of the pigment that carries oxygen (hemoglobin) in the red blood cells. The most common cause of hypochromia in the United States is not enough iron in the body (iron deficiency).

Hypochromia means that the red blood cells have less color than normal when examined under a microscope. This usually occurs when there is not enough of the pigment that carries oxygen (hemoglobin) in the red blood cells.
The most common cause of hypochromia in the United States is not enough iron in the body (iron deficiency). If it is not treated, this can lead to a disorder called iron deficiency anemia.
The cause of hypochromia should be evaluated by your health care provider.
Brittenham GM. Disorders of iron homeostasis: iron deficiency and overload. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 36.
Camaschella C. Microcytic and hypochromic anemias. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 15.
Updated by: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Change of spectral band position in the absorption, reflectance, transmittance, or emission spectrum of a molecule to a shorter wavelength (higher frequency).Wikipedia

- Bathochromic shift
Change of spectral band position in the absorption, reflectance, transmittance, or emission spectrum of a molecule to a longer wavelength (lower frequency). Also commonly called a red shift.Wikipedia
- Spectral line
Dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identify atoms and molecules.Wikipedia
- Absorption spectroscopy
Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field.Wikipedia
- Spectrophotometry
Branch of electromagnetic spectroscopy concerned with the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength. Spectrophotometry uses photometers, known as spectrophotometers, that can measure the intensity of a light beam at different wavelengths.Wikipedia
- Spectral signature
Variation of reflectance or emittance of a material with respect to wavelengths . The spectral signature of stars indicates the composition of the stellar atmosphere.Wikipedia
- Band emission
Fraction of the total emission from a blackbody that is in a certain wavelength interval or band. Ratio of the total emissive power of a black body from 0 to λ to the total emissive power over the entire spectrum.Wikipedia
- Spectral resolution
Measure of its ability to resolve features in the electromagnetic spectrum. Usually denoted by, and is closely related to the resolving power of the spectrograph, defined asWikipedia
- Discrete spectrum
Said to have a discrete spectrum if it takes only distinct values, with gaps between one value and the next. Characteristic set of discrete spectral lines seen in the emission spectrum and absorption spectrum of isolated atoms of a chemical element, which only absorb and emit light at particular wavelengths.Wikipedia
- Micro-spectrophotometry
Measure of the spectra of microscopic samples using different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation It is accomplished with microspectrophotometers, cytospectrophotometers, microfluorometers, Raman microspectrophotometers, etc. A microspectrophotometer can be configured to measure transmittance, absorbance, reflectance, light polarization, fluorescence (or other types of luminescence such as photoluminescence) of sample areas less than a micrometer in diameter through a modified optical microscope. Ability to measure the optical spectra of samples with a spatial resolution on the micron scale.Wikipedia
- Molecular electronic transition
Molecular electronic transitions take place when electrons in a molecule are excited from one energy level to a higher energy level. The energy change associated with this transition provides information on the structure of a molecule and determines many molecular properties such as colour.Wikipedia
- Spectral density
The power spectrum S_{xx}(f) of a time series x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed into a number of discrete frequencies, or a spectrum of frequencies over a continuous range.Wikipedia
- Photoacoustic effect
Formation of sound waves following light absorption in a material sample. In order to obtain this effect the light intensity must vary, either periodically (modulated light) or as a single flash (pulsed light).Wikipedia
- Optical depth
Natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material, and spectral optical depth or spectral optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted spectral radiant power through a material. Dimensionless, and in particular is not a length, though it is a monotonically increasing function of optical path length, and approaches zero as the path length approaches zero.Wikipedia
- Photoluminescence
Light emission from any form of matter after the absorption of photons (electromagnetic radiation). One of many forms of luminescence and is initiated by photoexcitation (i.e. photons that excite electrons to a higher energy level in an atom), hence the prefix photo-.Wikipedia
- Dicke effect
In spectroscopy, the Dicke effect, also known as Dicke narrowing or sometimes collisional narrowing, named after Robert H. Dicke, refers to narrowing of the Doppler broadening of a spectral line due to collisions the emitting species (usually an atom or a molecule) experiences with other particles. Atom is much smaller than the wavelength of the radiative transition, the atom changes velocity and direction many times during the emission or absorption of a photon.Wikipedia
- Spectroscopy
Study of the interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum; indeed, historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism.Wikipedia
- Reststrahlen effect
Reflectance phenomenon in which electromagnetic radiation within a narrow energy band cannot propagate within a given medium due to a change in refractive index concurrent with the specific absorbance band of the medium in question; this narrow energy band is termed the reststrahlen band. As a result of this inability to propagate, normally incident reststrahlen band radiation experiences strong-reflection or total-reflection from that medium.Wikipedia
- Monochromator
Optical device that transmits a mechanically selectable narrow band of wavelengths of light or other radiation chosen from a wider range of wavelengths available at the input. From the Greek roots mono-, 'single', and chroma, 'colour', and the Latin suffix -ator, denoting an agent.Wikipedia
- Absorbance
Common logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material, and spectral absorbance or spectral decadic absorbance is the common logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted spectral radiant power through a material. Dimensionless, and in particular is not a length, though it is a monotonically increasing function of path length, and approaches zero as the path length approaches zero.Wikipedia
- Absorption band
According to quantum mechanics, atoms and molecules can only hold certain defined quantities of energy, or exist in specific states. Atom or molecule, energy of the radiation changes the state of the atom or molecule from an initial state to a final state.Wikipedia
- Spectral purity
Term used in both optics and signal processing. In optics, it refers to the quantification of the monochromaticity of a given light sample.Wikipedia
- Photo-reflectance
Optical technique for investigating the material and electronic properties of thin films. Amplitude modulated light beam.Wikipedia
- Spectrohelioscope
Type of solar telescope designed by George Ellery Hale in 1924 to allow the Sun to be viewed in a selected wavelength of light. The name comes from Latin- and Greek-based words: Spectro, referring to the optical spectrum, Helio, referring to the Sun, and Scope, as in telescope.Wikipedia
- Spectroradiometer
Light measurement tool that is able to measure both the wavelength and amplitude of the light emitted from a light source. Spectrometers discriminate the wavelength based on the position the light hits at the detector array allowing the full spectrum to be obtained with a single acquisition.Wikipedia
- Dielectric spectroscopy
Dielectric spectroscopy (which falls in a subcategory of impedance spectroscopy) measures the dielectric properties of a medium as a function of frequency. Based on the interaction of an external field with the electric dipole moment of the sample, often expressed by permittivity.Wikipedia
- Astronomical spectroscopy
Study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light and radio, which radiates from stars and other celestial objects. A stellar spectrum can reveal many properties of stars, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.Wikipedia
- Normal mode
Oscillating system is a pattern of motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. The free motion described by the normal modes takes place at fixed frequencies.Wikipedia
- Zero-phonon line and phonon sideband
The zero-phonon line and the phonon sideband jointly constitute the line shape of individual light absorbing and emitting molecules (chromophores) embedded into a transparent solid matrix. When the host matrix contains many chromophores, each will contribute a zero-phonon line and a phonon sideband to the absorption and emission spectra.Wikipedia
Sentences forHypsochromic shift
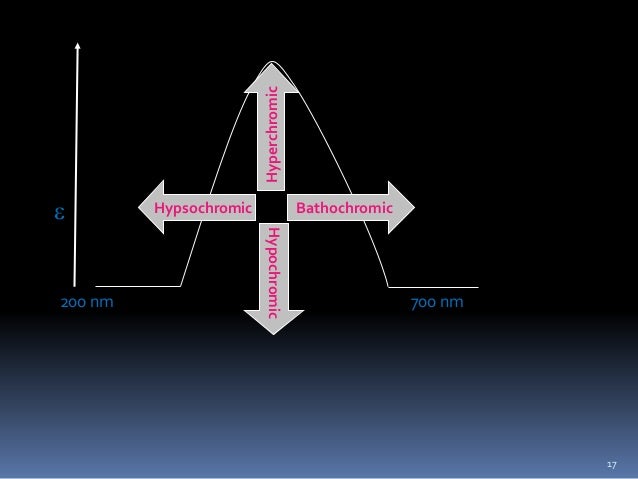

- Hypsochromic shift is a change to shorter wavelength (higher frequency).Bathochromic shift-Wikipedia
- Converting a parent azo dye to a Glycoazodye may produce a small hypsochromic shift in the absorption spectra.Glycoazodyes-Wikipedia
Hypsochromic Shift Is Also Called
This will create an email alert. Stay up to date on result for: Hypsochromic shift
